Did you know that Australia’s total exports grew by $1.77 billion in 2023, while imports climbed by $13.47 billion? This growth clearly highlights Australia’s active participation in global trade. However, behind these significant figures is a network of logistics and supply chain ensuring smooth trade.
In this article, we will explore the details of supply chains, including their key components, challenges, and opportunities. These elements play a vital role in shaping the global economy.
What is a Supply Chain?
A supply chain is a complex network that moves goods or services from their origin to their final destination. Also it involves organisations, people, and activities working together to ensure smooth and efficient operations. Moreover, global distribution chains expand this concept by connecting businesses and consumers across different countries and continents. These networks handle tasks such as sourcing raw materials, manufacturing products, and delivering them to end-users worldwide.
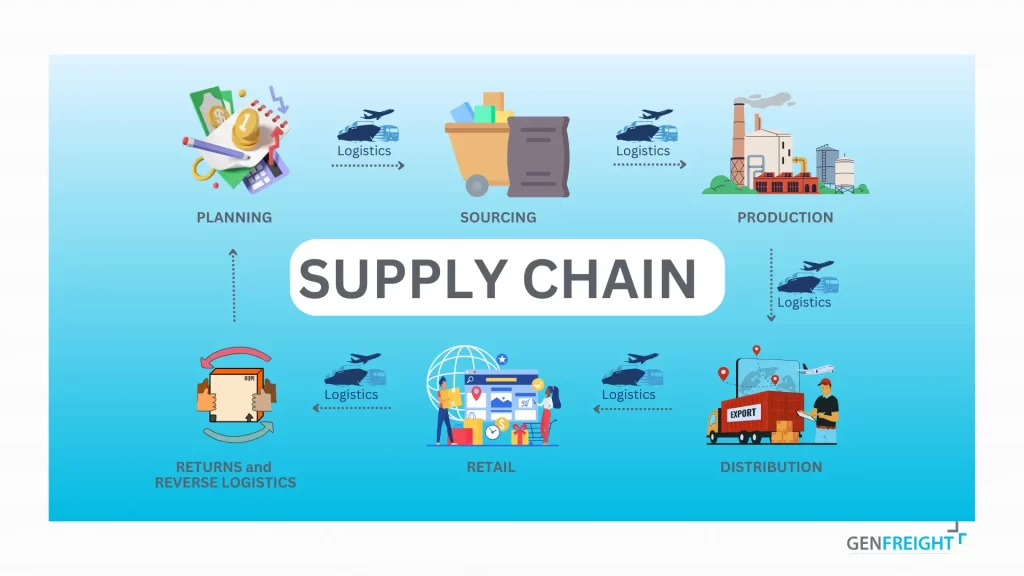
Core Components
A global supply chain is made up of several key components, each playing a vital role in the overall process:
- Planning. Firstly, this step involves forecasting demand, scheduling production, and allocating resources to meet future needs efficiently.
- Sourcing. Next component focuses on finding and choosing reliable suppliers to obtain raw materials and essential components.
- Production. After sourcing, this stage transforms raw materials into finished products through manufacturing, while ensuring consistent quality.
- Logistics. Meanwhile, logistics, often considered the core of the supply chain. In general it manages the movement of goods, including transportation, storage, and inventory control.
- Distribution. Then, it ensures finished products reach customers either directly or through established distribution channels.
- Customer Service. Additionally, this component includes assisting customers during the buying process, handling orders, answering questions, and managing returns.
- Returns and Reverse Logistics. Finally, it deals with returned products, recycling, or disposal while aiming to reduce environmental impact.
Why SCM is Important
What is supply chain management?
Supply chain management (SCM) is the art and science of designing, planning, executing, controlling, and monitoring supply chain activities. The main goals include creating value, gaining a competitive edge, and meeting customer needs effectively.
SCM is crucial for businesses for several reasons:
- Optimising Efficiency and Reducing Costs. Firstly, by streamlining processes, cutting waste, and shortening lead times, it helps businesses lower costs significantly.
- Improving Customer Satisfaction. Secondly, timely deliveries, accurate orders, and high-quality products ensure customer satisfaction. So effective supply chain management achieves these outcomes.
- Enhancing Supply Chain Visibility and Risk Management. Thirdly, by monitoring goods flow, businesses can identify risks early and take proactive steps to address them.
- Fostering Strong Supplier Relationships. Furthermore, collaborative supplier relationships lead to better quality, lower costs, and consistent on-time deliveries.
- Enabling Data-Driven Decision-Makin. Finally, through data analytics, businesses can gain valuable insights into performance and make informed decisions.
When implemented effectively, distribution chain management improves efficiency and enhances overall business success.
The Interplay of Supply Chain and Logistics
What is difference between supply chain and logistics?
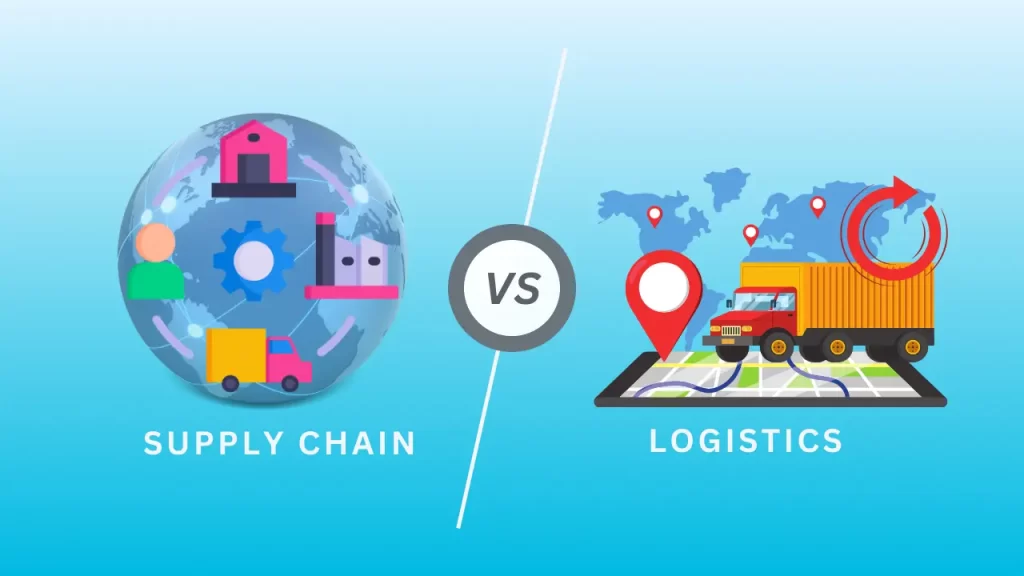
Although often used interchangeably, supply chain and logistics are distinct, yet closely linked concepts. A supply chain is a broader network involving all activities to bring a product or service from its beginning to its end use. In contrast, logistics is a part of supply chain management, focusing specifically on the physical movement, storage, and flow of goods and services.
To explain their relationship, consider this example: a t-shirt. The supply chain starts with sourcing raw materials (like cotton), manufacturing the fabric, cutting, sewing, and packaging the t-shirt. Meanwhile, logistics covers transporting raw materials to the manufacturing site, moving the finished t-shirt to a warehouse, and finally delivering it to the store or directly to the customer.
In short, logistics is the operational arm of the supply chain. It ensures goods move smoothly and efficiently from origin to consumption. By improving transportation, storage, and inventory management, logistics can greatly affect the overall performance of the supply chain.
A well-integrated distribution chain and logistics strategy can lead to several benefits:
- Reduced costs. Firstly, by simplifying processes, cutting waste, and optimising transport routes.
- Improved customer satisfaction. Moreover, by ensuring timely deliveries and accurate order fulfillment.
- Enhanced visibility. Additionally, by tracking goods flow and identifying potential delays.
- Increased agility. Finally, by adapting to changing market needs and customer demands.
Nowadays, businesses are increasingly operating on a global scale. As a result, global supply chains have become essential for sourcing raw materials, manufacturing products, and distributing goods to customers worldwide.
- Access to Diverse Resources. Firstly, distribution supply chains allow businesses to source raw materials and components from cost-effective, reliable suppliers worldwide.
- Lower Costs. Additionally, by leveraging economies of scale and accessing lower-cost labor markets, businesses can reduce production costs.
- Expanded Market Opportunities. Moreover, global supply chains enable businesses to reach new markets and customer segments, driving growth and increasing revenue.
To manage these challenges, businesses often rely on freight forwarders for help with international shipping. Freight forwarders offer a variety of services, including:
- International Shipping. Firstly, they arrange the transportation of goods by sea, air, or land.
- Customs Clearance. Secondly, they handle all customs procedures and documentation.
- Route Optimisation. Thirdly, they select the most efficient and cost-effective transportation routes.
- End-to-End Visibility. Lastly, they track shipments and provide real-time updates.
Undoubtedly, global supply chains face a range of risks and challenges that can disrupt operations and affect profitability. Some of the most common challenges include:
- Supply Chain Disruptions. For instance, natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, and pandemics can severely disrupt supply chains. A s a resilt they could cause delays, shortages, and increased costs.
- Tariff and Trade Barriers. Moreover, tariffs, quotas, and other trade restrictions can raise the cost of goods and create uncertainty for businesses.
- Currency Fluctuations. Additionally, changes in exchange rates can affect the profitability of international trade.
- Cybersecurity Threats. Furthermore, cyberattacks can compromise sensitive data, disrupt operations, and harm a company’s reputation.
- Ethical and Sustainability Concerns. Finally, as consumers demand ethical and sustainable products, businesses must ensure their supply chains align with these values.
Opportunities in International Trade and Logistics
Despite the challenges, global trade and logistics offer numerous opportunities for businesses:
- Technological Advancements. For example, technologies like IoT, AI, and blockchain are revolutionising supply chain management, enabling greater efficiency, transparency, and traceability.
- E-commerce Growth. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce has opened up new opportunities for businesses to reach global markets.
- Emerging Trends. Moreover, Industry 4.0, blockchain, and AI are driving innovation and transforming how businesses operate..
- Sustainable Supply Chain Practices. Furthermore, by adopting sustainable practices, businesses can reduce their environmental impact, enhance their brand reputation, and comply with increasingly strict regulations.
- Globalisation and Regionalisation. Finally, globalisation has created a more interconnected world. While regionalisation has led to the formation of regional trade blocs, offering new opportunities for businesses.

To reduce the risks and challenges associated with global supply chains, businesses need to implement strong strategies. Here are some key strategies:
- Diversification of Suppliers and Manufacturing Locations. By diversifying suppliers and manufacturing locations, businesses can reduce their reliance on a single source. Also by implementing this strategy companies can minimise the impact of disruptions.
- Comprehensive Risk Management Strategies. Additionally, developing comprehensive risk management plans, including contingency plans for various scenarios, helps businesses respond effectively to disruptions.
- Strong Supplier Relationships. Moreover, building strong relationships with suppliers improves collaboration, communication, and trust. As a result, this leads to more reliable and efficient supply chains.
- Digital Supply Chain Technologies. Furthermore, leveraging technologies like IoT, AI, and blockchain enhances visibility, improves decision-making, and increases the agility of supply chains.
- Sustainability Initiatives. Finally, adopting sustainable practices, such as reducing carbon emissions, minimising waste, and sourcing ethical materials, helps businesses build resilient and socially responsible supply chains.
Supply Chain Models
Different supply chain models can be used to optimise operations and meet specific business objectives. Some common models include:
- Continuous Flow Model. This model, for instance, works well for products with high demand and stable production processes. It primarily focuses on efficiency and cost reduction through continuous flow production.
- Fast Chain Model. In contrast, this model is ideal for products with short product life cycles and high demand variability. It prioritises speed and responsiveness to market changes.
- Flexible Chain Model. Moreover, this model adapts to fluctuations in demand and supply. It combines elements of both the continuous flow and fast chain models to strike a balance between efficiency and flexibility.
Logistics vs. SCM
Logistics is a subset of supply chain management that focuses on the physical movement, storage, and flow of goods and services. Specifically, it involves activities like transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and customer service.
On the other hand, SCM is a broader concept that includes all the activities involved in planning, executing, and controlling the flow of goods and services, from the point of origin to the point of consumption. So this encompasses sourcing, production, logistics, and customer service.
Why is Efficient Logistics Important?
Efficient logistics is crucial for the success of any business. It can help to:
- Reduce costs: By optimising transportation routes, minimising inventory levels, and improving warehouse efficiency.
- Improve customer satisfaction. By ensuring timely deliveries and accurate order fulfillment.
- Enhance supply chain visibility. By tracking the movement of goods and identifying potential bottlenecks.
- Mitigate risks. By having contingency plans in place to address disruptions.
Supply Chain Resilience
A resilient supply chain is one that can withstand disruptions and adapt to changing circumstances. It is characterized by three key attributes:
- Persistence: The ability to continue operations despite disruptions.
- Adaptation: The ability to adjust to changing conditions and adopt new strategies.
- Transformation: The ability to fundamentally change the supply chain to improve its resilience.
Logistics plays a critical role in building supply chain resilience. By diversifying transportation modes, building redundant supply chains, and implementing robust inventory management strategies, businesses can mitigate the impact of disruptions. For example, during a natural disaster, a resilient supply chain might involve rerouting shipments to avoid affected areas or drawing on buffer stocks to meet customer demand.
Social Responsibility in Supply Chains
In today’s increasingly conscious consumer market, social responsibility is no longer a mere buzzword but a critical factor in sustainable business practices. Undoubtedly, ethical sourcing, fair labor practices, and environmental sustainability are paramount for maintaining a positive brand reputation and fostering consumer trust.
Ethical Practices and Transparency:
- Fair Labor Standards. Firstly, ensuring that workers in the supply chain are paid fair wages, work in safe conditions, and are not subjected to forced labor or child labor.
- Ethical Sourcing. Secondly, sourcing materials from suppliers who adhere to ethical and sustainable practices.
- Thirdly, providing transparency into the supply chain, allowing consumers to trace the origin of products and understand the impact of their purchases.
Sustainable Logistics Practices:
- For instance, implementing energy-efficient practices in warehouses, such as using LED lighting and optimising storage layouts.
- Moreover, utilising low-emission vehicles for transportation to reduce carbon footprint.
- Finally, minimising packaging materials and using eco-friendly packaging solutions.

Emerging Trends and Technologies
The supply chain landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. As a result, some of the key emerging trends and technologies shaping the future of supply chain management include:
- Big Data Analytics. Firstly, using big data analytics to gain insights into supply chain performance, identify potential risks, and optimise decision-making.
• Digital Supply Chain Technologies: - IoT (Internet of Things). Also tracking and monitoring the movement of goods in real-time.
- AI (Artificial Intelligence). Additionally, automating tasks, optimising processes, and predicting future trends.
- Moreover, enhancing transparency, security, and traceability in supply chains.
- Design for Supply Chain (DFSC). Lastly, integrating supply chain considerations into the product design process to optimise product design and minimise costs.
For a more detailed exploration of these technologies and their transformative impact on supply chains, check out our article titled “Revolutionising Supply Chain Management: How Technology is Reshaping Logistics.”
Stakeholders
A successful distribution chain involves a diverse range of stakeholders, each playing a crucial role in the process. Specifically, these stakeholders include:
- Producers: The originators of raw materials or components.
- Vendors: Suppliers who provide goods or services to manufacturers or retailers.
- Manufacturers: Businesses that transform raw materials into finished products.
- Transporters: Companies responsible for moving goods from one location to another.
• Supply Chain Managers: Professionals who oversee and optimise the entire supply chain. - Retailers: Businesses that sell products directly to consumers.
- Consumers: The end-users of products and services.
In addition, effective collaboration and communication among these stakeholders are essential for a smooth-running supply chain.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of a global supply chain requires careful planning, efficient management, and strong partnerships. For instance, from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished products to consumers, each step in the supply chain is interconnected and impacts the overall performance of the business.
Logistics, as a critical component of the distribution chain, plays a vital role in ensuring the timely and cost-effective movement of goods. Therefore, by partnering with a reliable logistics provider like GenFreight Global Logistics, businesses can streamline their operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Furthermore, GenFreight offers a comprehensive range of logistics solutions, including transportation, warehousing, and customs clearance. With our expertise and global network, we can help businesses optimise their supply chains and achieve their business objectives.
