Did you know that global air cargo traffic saw a notable year-on-year increase of 10.8% in December 2023? According to an IATA report, this marked the largest annual growth in air cargo tonne-kilometers (CTKs) in the past two years.
Air freight is a key part of modern logistics. In fact, it has changed the way we trade and consume goods. With its unmatched speed and reliability, it helps businesses move high-value, time-sensitive, and perishable products across continents.
In this guide, we will explore air freight. First, we will look at its history, benefits, challenges, and important considerations for businesses. By the end of this article, you will understand how air freight works. Additionally, you will learn the factors that influence its cost and the steps involved in shipping goods by air.
A Brief History of Air Freight

The concept of air freight began in the early 20th century. In fact, the first cargo flight carried mail from Dayton to Columbus, Ohio, in 1910. By the 1940s, air freight became a key part of wartime logistics, enabling rapid transportation of critical supplies. Then, the 1960s marked a turning point with the introduction of dedicated cargo planes like the Boeing 747. These planes revolutionised capacity and efficiency. Since then, technological advancements, including GPS tracking and automated sorting systems, have streamlined operations. As a result, air freight is now a cornerstone of modern supply chains.
What is Air Freight?
In general, air freight is the transportation of goods via aircraft. In this process, a complex network of airlines, freight forwarders, customs brokers, and ground handlers work together. They move cargo from origin to destination. In particular, this mode of transportation is ideal for high-value, time-sensitive, or perishable goods. These goods require rapid delivery.
Why Choose Air Freight?
Air freight offers numerous advantages for businesses. As a result, it is a preferred shipping method in many cases:
- Speed. Firstly, it is the fastest mode of transportation, significantly reducing transit times compared to sea or road freight.
- Reliability. Secondly, air freight schedules are less prone to delays, ensuring timely delivery of goods.
- Remote Access. Thirdly, airplanes can reach remote or landlocked regions where other transport modes may not be viable.
- Safety. Finally, goods are less likely to get damaged or stolen during air transit, offering added security.
Challenges of Air Freight
While air freight offers numerous benefits, it also presents some challenges:
- Cost. Firstly, air freight is generally more expensive than sea or land freight due to higher fuel costs and operational expenses.
- Environmental Impact. Secondly, air freight contributes to carbon emissions, raising concerns about its environmental footprint.
- Regulatory Hurdles. Thirdly, air freight is subject to various regulations, including customs procedures, security screenings, and export controls. As a result, it can add complexity and delay shipments.
Understanding the Basics of Air Freight

To navigate the world of air freight, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental concepts and processes involved. Let’s now break down the key components:
Types of Air Freight
- Express Freight. Express freight is designed for high-speed, time-sensitive shipments. In particular, it is ideal for urgent deliveries, such as medical supplies or critical components, where every minute counts. Also these shipments typically use dedicated services with guaranteed delivery times.
- General Cargo. General cargo includes routine shipments that do not need special handling or urgency. For example, common items include clothing, machinery parts, or non-perishable consumer goods. It offers a cost-effective solution for businesses with less time-sensitive needs.
- Specialised Cargo. This category includes goods requiring specific handling. These goods might be perishable items like fresh produce or seafood, hazardous materials like chemicals, and high-value items like electronics. Specialised cargo often involves temperature-controlled environments or strict safety and regulatory requirements.
Key Players in the Air Freight Process
Understanding the terminology used in air freight is crucial for navigating the process effectively:
- Shipper. The party or business responsible for sending the goods.
- Consignee. The recipient of the goods at the destination.
- Forwarder. A logistics provider that arranges transportation, documentation, and customs clearance on behalf of the shipper.
- Carrier. The airline or shipping company responsible for transporting the goods.
- Customs Broker. A specialist who handles customs clearance procedures, ensuring compliance with import and export regulations.
The Air Freight Process
In general, the air freight process involves several critical stages to ensure smooth transportation and delivery of goods:
- Booking and Scheduling. Firstly, the process begins with selecting a carrier, booking cargo space, and scheduling pickup. So businesses can work directly with carriers or through freight forwarders for a seamless experience.
- Pickup and Delivery. Secondly, goods are collected from the shipper’s location and transported to the airport. Additionally, proper packaging and labeling are essential to ensure the shipment is ready for transit.
- Customs Clearance. Thirdly, customs formalities include submitting documentation, such as invoices, packing lists, and air waybills, and undergoing inspections if required. A customs broker often handles this stage.
- Transportation and Handling. Moreover, once cleared, goods are loaded onto the aircraft and transported to the destination airport. Upon arrival, they are unloaded and processed for delivery.
- Delivery. Lastly, the final stage involves delivering the goods to the consignee. This step may include last-mile delivery services to reach the recipient’s specified location.
How is air freight cost calculated
To accurately calculate air freight rates, it’s essential to consider several factors. As a result, that can significantly impact the final cost of shipping your goods.
Factors Affecting Air Freight Rates
1.Weight and Volume:
- Actual Weight: The physical weight of the shipment.
- Dimensional Weight: A calculated weight based on the dimensions (length, width, and height) of the shipment. Usually carriers use dimensional weight to determine the chargeable weight. But chargeable weight is often higher than the actual weight for bulky items.
- Distance. Also the distance between the origin and destination airport directly influences the cost of transportation.
- Fuel Surcharges. Moreover, carriers often impose additional charges based on fluctuations in fuel prices.
- Security Fees. Additionally, security screenings and measures add to the overall cost of air freight.
- Insurance Costs. Finally, insuring your shipment against loss or damage during transit is crucial. And the cost of insurance varies based on the value of the goods.
How to Calculate Air Freight Rates

1.Volumetric (dimensional) Weight Calculation.
- Formula
Dimensional Weight = (Length x Width x Height) / Dimensional Weight Factor
- Dimensional Weight Factor. This factor varies by carrier but is typically around 5 – 6,000 cubic centimeters per kilogram.
- Chargeable Weight. The higher of the actual weight and dimensional weight is used to calculate the freight rate.
Example
Let’s say you have a package with the following dimensions:
- Length: 100 cm
- Width: 50 cm
- Height: 40 cm
- Actual weight: 20 kg
Calculating the dimensional weight:
(100 x 50 x 40) / 6000 = 33.33 kg
Since the dimensional weight (33.33 kg) is higher than the actual weight (20 kg), the chargeable weight will be 33.33 kg.
2.Using Online Freight Calculators.
- Also many carriers and freight forwarders offer online freight calculators that allow to estimate rates based on the shipment’s details.
- These tools can provide a quick and easy way to get a rough estimate of the cost.
3.Working with a Freight Forwarder:
- Undoubtedly, freight forwarders have established relationships with carriers and can negotiate favorable rates on your behalf.
- They can also provide expert advice on packaging, documentation, and customs clearance, helping you to minimise costs and avoid delays.
Packaging and Labeling
Proper packaging and labeling are essential for ensuring that goods arrive safely and comply with air freight regulations. In addition, adhering to these guidelines helps prevent damage and delays during transit.
Packaging Guidelines
Effective packaging is the foundation of successful air freight shipments. Therefore, follow these best practices:
1.Choosing the Right Packaging Materials:

- Cardboard Boxes. A versatile option for most general cargo. However, ensure they are sturdy and well-sealed.
- Wooden Crates. Ideal for heavy or fragile items. So they offer superior protection against shock and vibration.
- Pallets. Used for consolidating multiple items to simplify handling. Also they reduce the risk of damage.
2.Proper Packaging Techniques:
- Cushioning. Firstly, use appropriate cushioning materials like bubble wrap, foam, or packing peanuts to protect your goods from impact and movement.
- Sealing. Secondly, securely seal your packages with strong tape to prevent accidental opening.
- Weight Distribution. Thirdly, distribute the weight evenly within the package to avoid stress on any particular area.
Labeling and Marking
- Clear and Accurate Labeling:
- Shipper and Consignee Information. Firstly, include the full names, addresses, and contact information of both parties.
- Weight and Dimensions. Secondly, indicate the weight and dimensions of the package to aid in handling and transportation.
- Content Description. Thirdly, provide a detailed description of the contents to facilitate customs clearance and insurance claims.
- Handling Instructions:
- Fragile. Clearly mark fragile items to alert handlers to exercise caution.
- This Side Up. Additionally, indicate the correct orientation for the package.
- Keep Dry. Moreover, for goods sensitive to moisture, use waterproof packaging and clearly mark the package.
- Adhering to International Labeling Standards. For goods subject to specific regulations, such as hazardous materials , follow the IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR). These standards mandate standardised labels, including hazard symbols, UN numbers, and handling instructions for safe air transport.
Airlines vs. Freight Forwarders
When shipping goods by air, you have the option of working directly with an airline or utilising the services of a freight forwarder. So let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of each:
Airline Options
- Major Airlines. Usually many commercial airlines have dedicated cargo divisions. These divisions utilise the cargo hold of passenger flights or operate specialised freighter aircraft. Examples include Emirates SkyCargo, Qantas Freight, and Lufthansa Cargo. In addition, these airlines often have extensive global networks and offer reliable services for standard and express shipments.
- Specialised Cargo Airlines. These airlines focus solely on air freight, offering specialised services for various types of cargo. For example, they handle perishable goods, hazardous materials, and oversized shipments. Examples of such airlines include FedEx Express, UPS Airlines, and DHL Express.
Benefits of Using a Freight Forwarder
Freight forwarders act as middlemen between shippers and carriers, making the logistics process easier and offering several key advantages:
- Expertise and Experience. Firstly, freight forwarders have in-depth knowledge of shipping regulations, documentation requirements, and industry best practices. So their expertise ensures compliance and minimises the risk of delays or errors.
- Network and Connections. Secondly, with a global network of agents and partnerships with airlines, freight forwarders can get good rates. Additionally, they have access to many routes. This network helps them offer backup solutions if problems arise.
- Consolidated Shipments. Thirdly, forwarders often consolidate multiple shipments from different businesses into a single cargo load. This process, known as consolidation, reduces costs by sharing transportation expenses among multiple shippers.
- Customs Clearance Assistance. Moreover, navigating customs regulations can be complex. However, freight forwarders handle all aspects of customs clearance, including documentation, duties, and inspections, ensuring a smooth process.
- Insurance Coverage. Lastly, many forwarders offer cargo insurance to protect shipments against loss, damage, or theft. Consequently, this insurance gives peace of mind and financial protection for valuable goods.
Unique Challenges

Undoubtedly, air freight to and from Australia presents unique challenges due to the country’s geographic isolation and stringent regulations:
- Remote Locations and Infrastructure. Firstly, Australia’s vast size and limited infrastructure can impact transportation times and costs. Therefore, it’s important to plan accordingly.
- Strict Customs Regulations and Quarantine Restrictions. Secondly, the Australian Border Force (ABF) imposes strict customs and quarantine regulations to protect the country’s environment and economy. As a result, shipments may face additional checks or delays.
- Time Zone Differences. Thirdly, significant time zone differences between Australia and other countries can complicate communication and coordination. Consequently, it may take longer to resolve issues or get updates.
Tips for Successful Air Freight to and From Australia
To ensure smooth and efficient air freight to and from Australia, consider the following tips:
- Work with Experienced Freight Forwarders. Partner with freight forwarders who have a strong presence in Australia and a deep understanding of local customs regulations, quarantine requirements, and logistics challenges.
- Plan Ahead. Additionally, allow sufficient time for customs clearance and delivery, especially during peak seasons or when shipping to remote locations.
- Understand and Comply with Australian Customs Regulations. Moreover, familiarise yourself with the specific requirements for importing and exporting goods to and from Australia. Otherwise, misdeclaration or non-compliance can lead to significant delays, fines, or even seizure of goods.
- Consider Seasonal Factors and Holidays. Lastly, seasonal factors, such as weather conditions and holidays, can impact shipping times. For instance, increased demand during Christmas or delays caused by cyclones in Northern Australia should be factored into your shipping timeline.
Additional Considerations for Air Freight
While air freight offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to consider the broader implications of this mode of transportation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
- Environmental Impact of Air Freight. Firstly, air freight has a higher carbon footprint compared to other transportation modes, such as sea freight. Aircraft emissions contribute significantly to greenhouse gases, making sustainability a growing concern.
- Sustainable Options. Secondly, businesses can reduce their environmental impact by:
- Opting for carbon offset programs that compensate for emissions.
- Using eco-friendly packaging materials like biodegradable or recycled products.
- Consolidating shipments to maximise cargo space and minimise unnecessary flights.
- Industry Initiatives. Thirdly, airlines and logistics providers are adopting green logistics practices. For example investing in fuel-efficient aircraft, utilising renewable energy at facilities, and implementing advanced technologies to reduce emissions. Also programs like the International Air Transport Association’s (IATA) sustainability initiatives aim to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050.
Insurance
Insurance is crucial to protect your shipment against loss or damage during transit. Therefore consider the following types of coverage:
- All-Risk Insurance. Provides comprehensive coverage against various risks, including loss, damage, theft, and natural disasters.
- Specific All-Risk Insurance. Covers specific types of loss or damage, such as breakage, spillage, or contamination.
Security and Safety
1.Security Measures. Firstly, the air freight industry employs robust security protocols, including:
- Screening cargo for prohibited or dangerous items.
- Using advanced surveillance systems to monitor facilities.
- Implementing tamper-evident seals to secure shipments.
2.Protection Against Theft and Damage. Secondly, secure packaging, proper labeling, and selecting trusted carriers are additional ways businesses can protect their shipments.
Emerging Trends in Air Freight
- Drone Delivery. Drones are revolutionising last-mile delivery by enabling fast, efficient transport of smaller packages. Moreover, they are particularly effective in delivering goods to remote or hard-to-reach locations.
- Blockchain Technology. Blockchain enhances supply chain transparency by creating a permanent record of transactions. Additionally, it helps track shipments in real time, prevents fraud, and improves accountability among stakeholders.
- E-commerce and Air Freight. Also the rapid growth of e-commerce has increased demand for air freight. Consequently, online retailers prioritise speed, making air freight a preferred choice for meeting customer expectations for fast delivery.
- Sustainability and Green Logistics. Businesses are increasingly adopting green logistics practices to align with consumer demand for environmentally friendly operations. Furthermore, reducing carbon emissions and utilising sustainable packaging materials are becoming standard practices in the industry.
Air Freight vs. Sea Freight
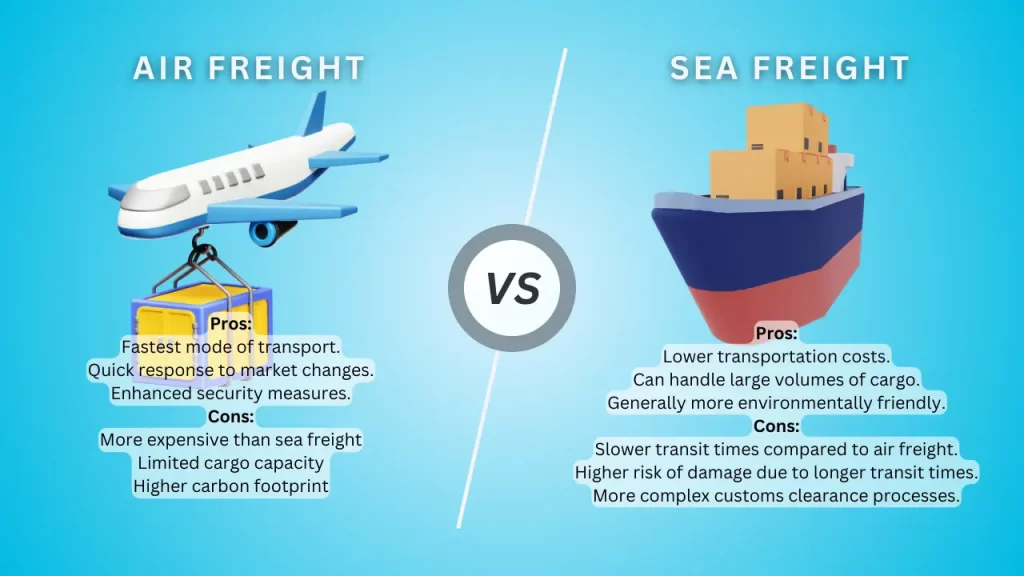
Choosing between air freight and sea freight depends on several factors, such as cost, speed, cargo type, and environmental impact. Therefore, understanding these differences helps businesses make better decisions that suit their logistics needs.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Air Freight: Air freight provides fast delivery, making it perfect for high-value, time-sensitive, and perishable goods. However, it is usually more costly than sea freight.
- Sea Freight: On the other hand, sea freight is a more affordable option for bulk shipments of low-value, non-perishable goods. However, it takes much longer for transit.
Cargo Sensitivity and Special Requirements
- Air Freight: Air freight is well-suited for perishable goods, high-value items, and urgent shipments. In addition, it offers controlled temperature and humidity conditions to protect sensitive cargo.
- Sea Freight: Sea freight, meanwhile, is great for bulk commodities, non-perishable goods, and shipments that are less urgent. It is also commonly used for heavy and oversized cargo.
Insurance and Risk Management
- Air Freight: Insurance costs can be higher for air freight due to the risks of air transport. However, there is comprehensive insurance to protect against loss, damage, and delays.
- Sea Freight: In contrast, sea freight generally has lower insurance costs. However, the risk of damage or loss is higher due to the longer transit times and exposure to various hazards.
Customs Clearance and Documentation
- Air Freight: Customs clearance is often quicker and more efficient for air freight, especially for express shipments. However, strict security measures and documentation requirements can add complexity.
- Sea Freight: On the other hand, customs clearance for sea freight can take longer and be more complicated, particularly for large shipments and goods that are subject to duties and tariffs.
Supply Chain Flexibility and Agility
- Air Freight: Air freight offers greater flexibility and agility, allowing businesses to quickly respond to market changes and customer demands.
- Sea Freight: Conversely, sea freight offers a more predictable and stable supply chain. But it may be slower in responding to sudden changes in demand.
Environmental Impact
- Air Freight: Air freight significantly contributes to carbon emissions, making it less eco-friendly. However, advancements in aircraft technology and sustainable aviation fuels are helping reduce the industry’s carbon footprint.
- Sea Freight: In comparison, sea freight generally has a lower carbon footprint per unit of cargo than air freight. However, concerns remain about marine pollution and the environmental effects of shipping on marine ecosystems.
Conclusion
Air freight has transformed global trade, offering unparalleled speed and reliability for the transportation of goods. By understanding the key factors influencing air freight costs, processes, and challenges, businesses can optimise their supply chain operations and ensure the timely delivery of their products.
To maximise the benefits of air freight, it’s essential to seek professional advice from experienced freight forwarders. At GenFreight, we offer comprehensive services that cover every aspect of the air freight process. We handle carrier selection based on your specific needs, manage customs clearance, provide warehousing solutions, and arrange door-to-door delivery, ensuring a seamless and efficient shipping experience.
Contact us for tailored solutions that align with your shipping requirements and optimise your supply chain operations.
